Heart Disease Symptoms in Women: Know the Preventions
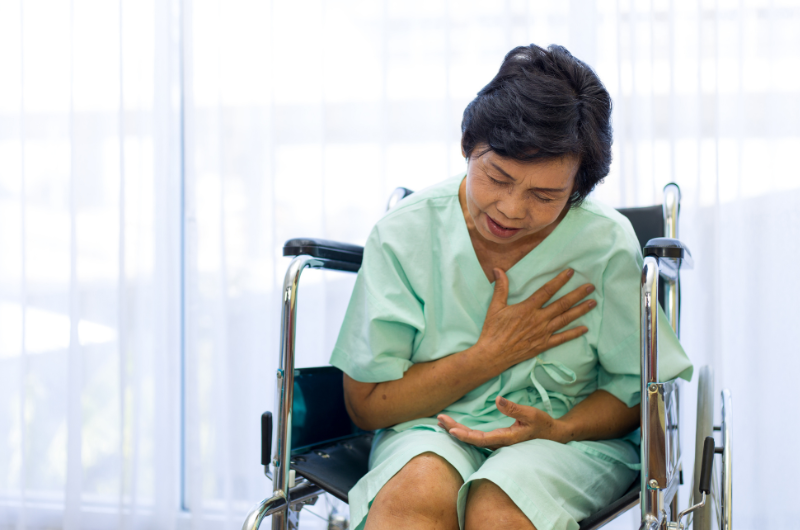

Heart disease is the leading cause of death among women globally, yet its symptoms often go unrecognized. Unlike men, women may experience heart disease with less obvious symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management. This article explores the symptoms of heart disease in women and offers natural remedies and herbs for prevention and healing.
1. Recognizing the Symptoms
Common Symptoms of Heart Disease in Women
Women often experience heart disease symptoms that differ from men. These include:
- Unexplained Fatigue: Persistent and unusual fatigue, even after adequate rest.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Indigestion or Nausea: Unexplained indigestion, heartburn, or nausea.
- Pain in the Neck, Jaw, Throat, or Upper Abdomen: Discomfort that can be mistaken for other conditions.
Understanding these symptoms and their subtlety is crucial for timely intervention.
The Importance of Listening to Your Body
Women should trust their instincts and seek medical advice if they notice unusual symptoms. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
2. The Role of Lifestyle in Heart Health
Diet and Heart Health
Adopting a heart-healthy diet can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
- The Mediterranean Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats like olive oil. Studies show it can reduce heart disease risk by up to 30% .
- Foods Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Incorporate salmon, flaxseeds, and walnuts to support heart health.
Exercise and Its Benefits
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy heart.
- Types of Exercises: Walking, yoga, and swimming are excellent for cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week .
3. Natural Remedies and Healing Herbs
Herbs for Heart Health
Several herbs can support cardiovascular health naturally.
- Hawthorn: Known for improving cardiovascular function and reducing blood pressure. Studies have shown its effectiveness in treating heart failure .
- Garlic: Lowers cholesterol levels and blood pressure. A meta-analysis confirmed its benefits in cardiovascular health .
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, an anti-inflammatory compound beneficial for heart health .
- Ginger: Reduces cholesterol and prevents blood clotting, supporting overall heart health .
Home Remedies to Consider
- Lemon and Honey Tea: A simple remedy to support heart health. Lemon is rich in vitamin C, and honey provides antioxidants.
- Flaxseed and Chia Seed Pudding: High in Omega-3 fatty acids, these seeds help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Green Tea: Known to improve blood flow and reduce cholesterol levels. Its antioxidants support overall cardiovascular function .
4. Stress Management Techniques
Mindfulness and Meditation
Reducing stress is vital for heart health. Mindfulness practices can significantly lower stress levels and improve heart health.
- Simple Meditation Practices: Regular meditation can reduce blood pressure and enhance emotional well-being .
Yoga and Breathing Exercises
Yoga and breathing exercises offer physical and mental health benefits.
- Specific Yoga Poses: Poses like the Downward Dog and Bridge Pose can support heart health.
- Pranayama Breathing Exercises: Techniques like deep breathing and alternate nostril breathing reduce stress and improve cardiovascular function .
5. The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular Health Screenings
Routine check-ups are essential for early detection and management of heart disease.
- Screenings for Blood Pressure, Cholesterol, and Glucose Levels: Regular monitoring helps in early intervention and management .
Understanding Your Numbers
Knowing your health metrics can help you manage your heart health better. Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure you stay informed about your cardiovascular health.
6. Creating a Heart-Healthy Environment
Building a Support System
A strong support system can significantly impact heart health.
- Role of Family and Friends: Encouragement from loved ones can promote healthy lifestyle changes.
- Joining Support Groups: Community health initiatives provide valuable resources and support for maintaining heart health.
Healthy Habits at Home
Creating a heart-healthy environment at home can make a big difference.
- Reducing Exposure to Environmental Toxins: Avoiding harmful substances and ensuring a clean living environment support heart health.
Conclusion
Empowerment Through Knowledge
Educating oneself about heart disease is the first step towards prevention and management. Natural remedies and lifestyle changes can play a significant role in maintaining heart health.
Final Thoughts
Heart disease is manageable with the right approach. By incorporating natural remedies and making informed lifestyle choices, women can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease.
- Suggested Reading and Resources:
References
- struch, R., et al. “Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet.” New England Journal of Medicine, 2013.
- Sofi, F., et al. “Mediterranean diet and health status: an updated meta-analysis and a proposal for a literature-based adherence score.” Public Health Nutrition, 2014.
- Penedo, F. J., & Dahn, J. R. “Exercise and well-being: a review of mental and physical health benefits associated with physical activity.” Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 2005.
- Pittler, M. H., & Ernst, E. “Hawthorn extract for treating chronic heart failure: meta-analysis of randomized trials.” American Journal of Medicine, 2008.
- Ried, K., et al. “Effect of garlic on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2008.
- H.K.Bakhru (1992) Herbs That Heal: Natural Remedies for Good Health. Orient Paperbacks. Delhi, India.
- T.V.Sairam (1999) Home Remedies Vol-II: A Handbook of Herbal Cures for Common Ailments. Penguin Books India.
Dos
Do eat a heart-healthy diet: Consume plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in fish, nuts, and olive oil.
Do exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Do manage stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to lower stress levels and improve heart health.
Do get enough sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support overall health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Do maintain a healthy weight: Keep your body mass index (BMI) within a healthy range by following a balanced diet and staying physically active.
Do monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels: Regularly check these vital signs and consult with your healthcare provider to keep them within healthy ranges.
Do stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support cardiovascular function and overall health.
Do incorporate heart-healthy herbs and spices: Include herbs like garlic, ginger, turmeric, and cayenne pepper in your diet to promote heart health naturally.
Do practice portion control: Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating, which can contribute to weight gain and heart disease risk.
Do seek regular medical check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider for routine check-ups and screenings to detect any potential heart health issues early.
Don’ts
Don’t smoke or use tobacco products: Smoking increases the risk of heart disease and other serious health conditions. If you smoke, seek support to quit, and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
Don’t consume excessive alcohol: Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, as excessive drinking can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease.
Don’t rely solely on supplements: While certain supplements may have benefits for heart health, they should not replace a healthy diet or lifestyle. Consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
Don’t neglect mental health: Mental health conditions like depression and chronic stress can negatively impact heart health. Seek support and treatment if you’re struggling with mental health issues.
Don’t consume excessive processed or fried foods: These foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sodium, and added sugars, which can contribute to heart disease risk.
Don’t ignore symptoms: Pay attention to any signs or symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or dizziness, and seek medical attention promptly if you experience them.
Don’t skip medications: If you’ve been prescribed medication for heart health, take it as directed by your healthcare provider, even if you’re feeling well.
Don’t engage in sedentary behavior: Limit sitting for prolonged periods and aim to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine to support heart health.
Don’t ignore sleep problems: Address any sleep issues, such as insomnia or sleep apnea, as they can increase the risk of heart disease and other health problems.
Don’t neglect regular dental care: Oral health is linked to heart health, so maintain good oral hygiene habits and schedule regular dental check-ups.
Send Us A Message
FAQs
- Common symptoms of heart disease in women include unexplained fatigue, shortness of breath, indigestion or nausea, and pain in the neck, jaw, throat, or upper abdomen.
- Heart disease symptoms in women can be more subtle and less recognizable than in men. Women may experience symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, or jaw pain rather than the typical chest pain often associated with heart attacks in men.
- Yes, certain herbs and natural remedies may help support heart health and manage symptoms of heart disease. Herbs like hawthorn, garlic, turmeric, and ginger have been studied for their potential cardiovascular benefits.
- It's recommended to have regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your heart health. Your doctor can advise you on how often you should have screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors based on your age, medical history, and lifestyle.